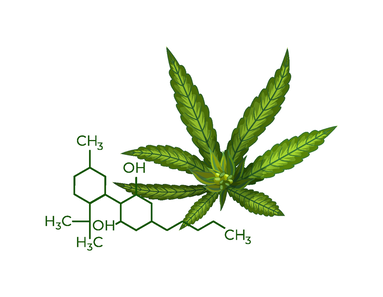
 Cannabinoids are a diverse group of chemical compounds that are naturally found in the cannabis plant (Cannabis sativa). They interact with the endocannabinoid system in the human body and in other animals, modulating various physiological processes. The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex cell-signaling system present in the bodies of all vertebrate animals. It plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis, which is the internal balance necessary for organisms to function properly. The ECS is involved in regulating processes such as:
There are three primary types of cannabinoids:
The interaction between cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system is complex and involves various receptors, primarily CB1 and CB2 receptors. CB1 receptors are primarily found in the brain and central nervous system, while CB2 receptors are more prevalent in the peripheral tissues and the immune system. Cannabinoids have garnered significant interest due to their potential therapeutic properties, such as pain relief, anti-inflammatory effects, anti-anxiety properties, and potential neuroprotective effects. However, more research is needed to fully understand their mechanisms of action and their specific therapeutic applications. As a result, the use of cannabinoids for medical purposes is a subject of ongoing research.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
Tanya's thoughts
Some of these articles are about my life, others are summaries from my research. Let me know what you'd like to learn about by writing to [email protected]. Thanks! Archives
May 2024
Categories |
Visit us! Ridge Hemp Wellness
15 Main St., Littleton, NH
Phone: 339-707-0628
About Ridge Hemp
Contact us
15 Main St., Littleton, NH
Phone: 339-707-0628
About Ridge Hemp
Contact us

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed